벡터를 모니터 점으로 표현하기
스크린 좌표계 :
- 데카르트 좌표계를 사용
- y축이 아래를 향하는 방식
- 이산적인 정수를 사용
- 픽셀 Pixel : 스크린 좌표계에서 좌표와 색상에 대응하는 화면 요소
- 픽셀화 Rasterization : 실수로 표현된 벡터좌표를 정수로 변환 후 색상을 부여하는 과정
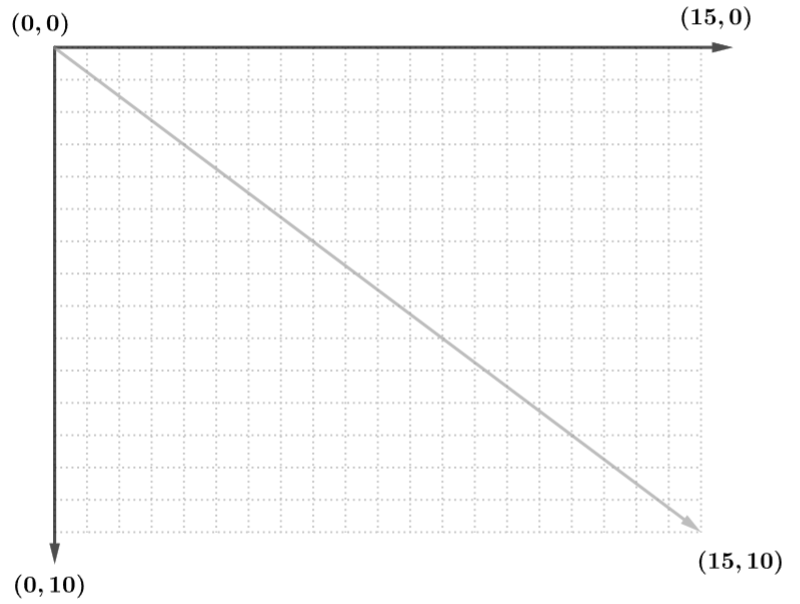
*픽셀화 과정에서는 경계값에 대한 픽셀화 규칙이 필요하다.해상도가 짝수인 경우 원점을 픽셀로 표현해야할때 , 가장자리에 벡터 좌표가 걸쳐져 있는 경우 규칙을 정해야 한다.
반대로 스크린 좌표에서 데카르트 좌표로 변환할때도 규칙이 필요하다.
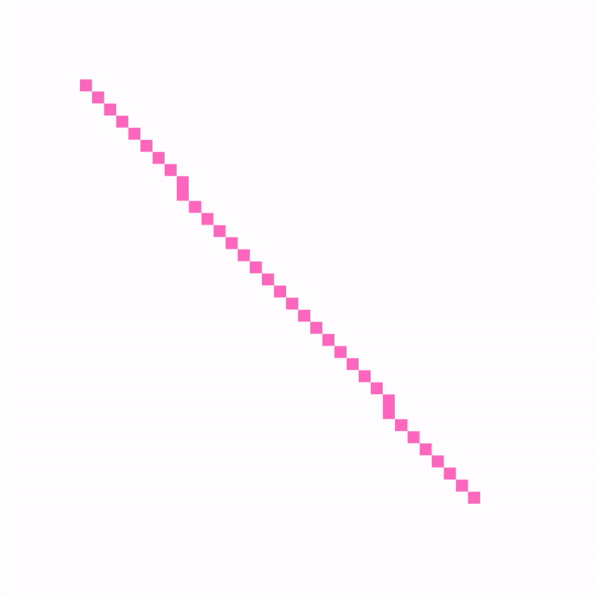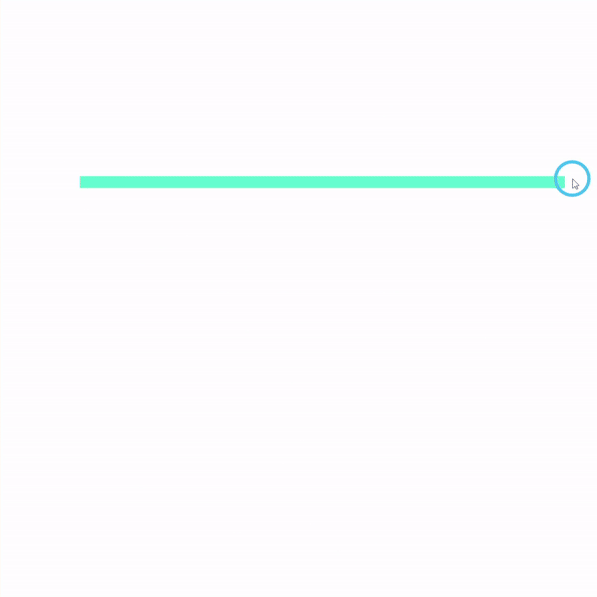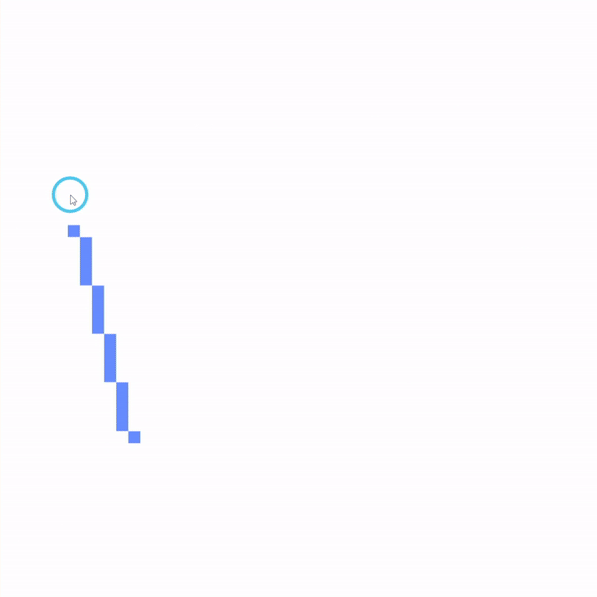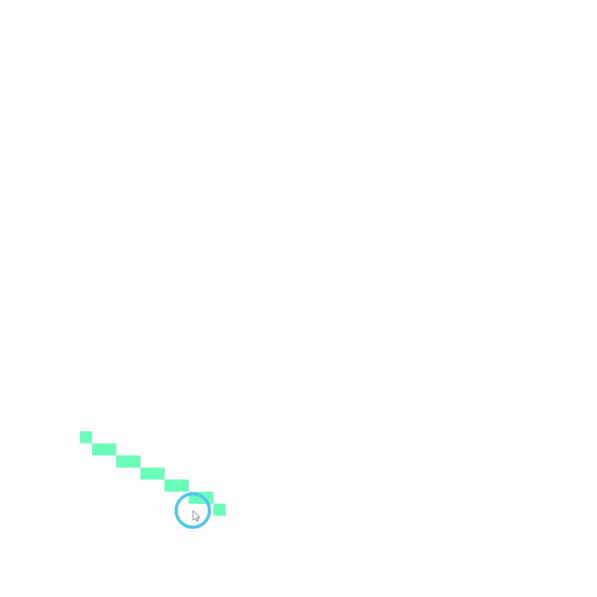
브레젠험 알고리즘 Bresenham's algorithm
두점에서 스칼라 a 값의 범위를 늘리면서 벡터를 생성하고 대응하는 픽셀을 찍는다면 하나의 픽셀에 대응되는 벡터가 많기 때문 효과적이지 못하기 때문에 픽셀로 된 선을 그리는 알고리즘이 따로 있다.
브레젠험 알고리즘은 화면을 8등분 영역으로 구분한 후 각 영역별로 그려내는 방식을 사용한다.
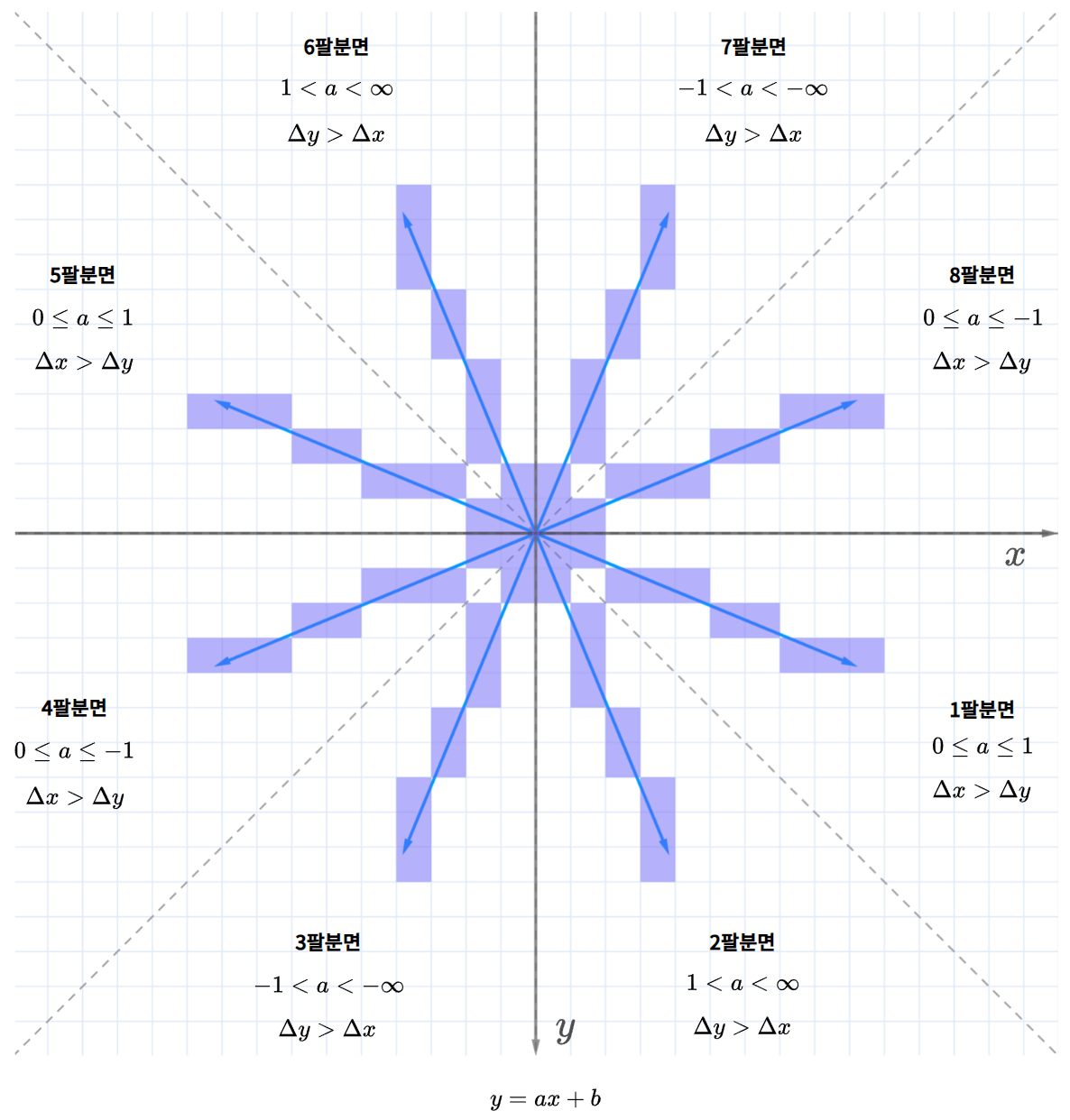
1팔분면에 해당하는 선의 예시로 살펴보자.
1팔분면은 [$0^\circ,45^\circ $]의 범위를 가진다.
이는 해당 영역에 존재하는 모든 선의 기울기가 1을 넘을 수 없음을 의미하며 1팔분면에 위치한 선을 구성하는 점의 진행은 평행하거나 한칸만 아래로 내려가는 특징이 있다.
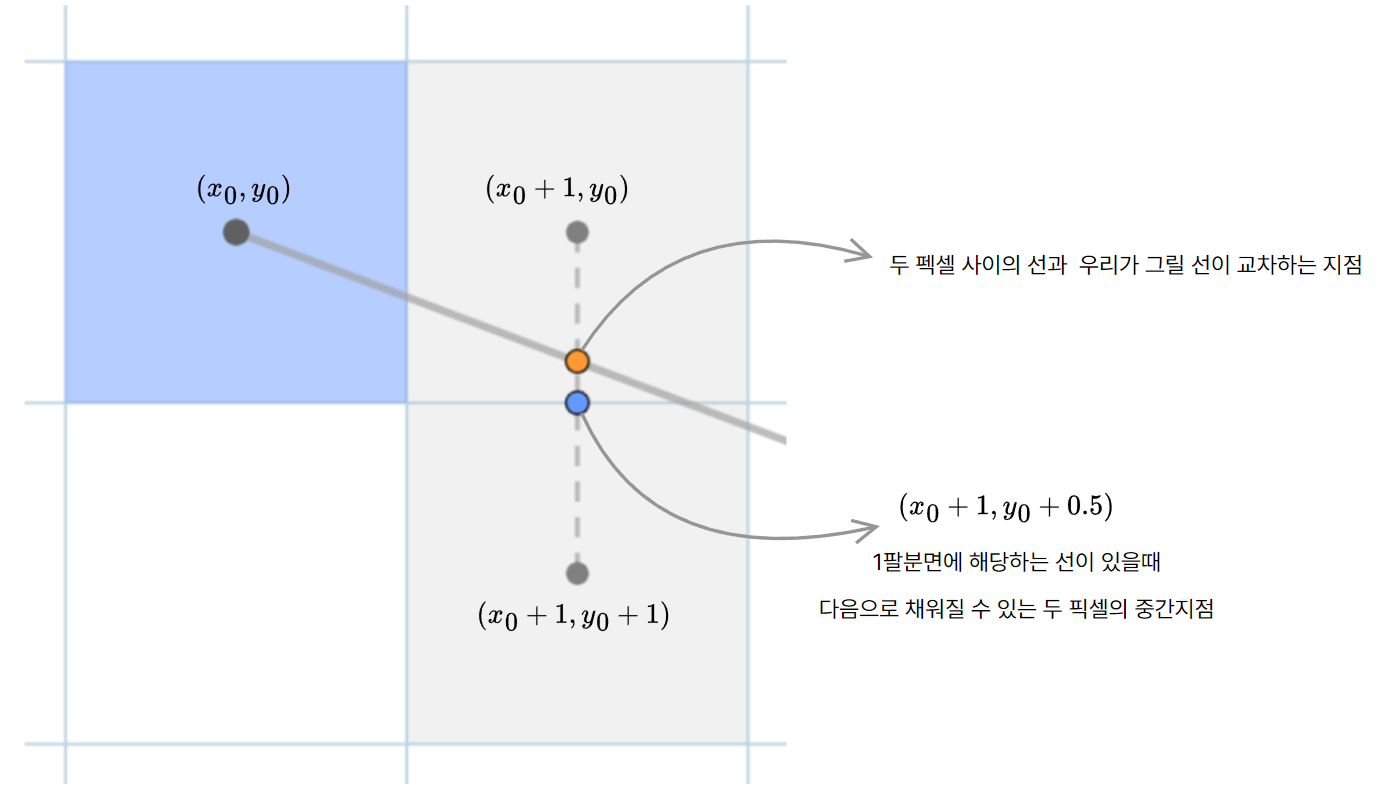
교차점●이 위 두픽셀의 중간지점 ●보다 위에 있다면 $(x+0+1,y_0)$ 픽셀을 칠하고 아래에 있다면 $(x+0+1,y_0+1)$ 픽셀이 칠해진다. ● y값 > ● y값
이를 수식으로 표현하기위해 직선의 방정식 $y= ax+b$에 시작 좌표값을 대입해서 확인해보자
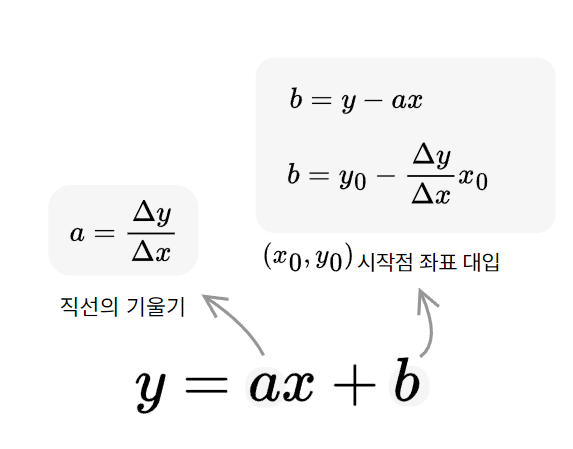
$y=\frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}x+b$
● $\frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}x+y_1-\frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x} x_1 <$ ● $ y_0+0.5$
이를 단순화 하면 아래와 같다.
$2\Delta y-\Delta x<0$
각 지점의 값을 대입한 판별값은 아래와 같은 패턴으로 증가한다.
유니티로 브레젠험 알고리즘을 활용해서 선그리기
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class DrawLine : MonoBehaviour
{
public Material mat;
private Texture2D texture;
public int height = 50;
public int width = 50;
private int y0;
private int x0;
private Vector2Int endPos;
private List<Vector2Int> container;
private Color[] texturePixelsColors;
private Color rc;
private Vector2 startPos;
void Start()
{
x0 = (int)(width * .5f);
y0 = (int)(height * .5f);
endPos = new Vector2Int(width, height);
texture = new Texture2D(height, width, TextureFormat.RGBA32, true);
texture.wrapMode = TextureWrapMode.Clamp;
texture.filterMode = FilterMode.Point;
texturePixelsColors = new Color[height * width];
for (int i = 0; i < texturePixelsColors.Length; i++)
{
texturePixelsColors[i] = new Color(1, 1, 1);
}
texture.SetPixels(texturePixelsColors);
texture.Apply();
mat.mainTexture = texture;
}
private Renderer rend;
private MeshCollider meshCollider;
private Texture2D tex;
private RaycastHit hit;
private Vector2 startUV;
private Vector2 endUV;
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
{
rc = Color.HSVToRGB(Random.Range(0f, 1f), 0.6f, 1);
if (!Physics.Raycast(Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition), out hit))
return;
rend = hit.transform.GetComponent<Renderer>();
meshCollider = hit.collider as MeshCollider;
if (rend == null || rend.sharedMaterial == null || rend.sharedMaterial.mainTexture == null ||
meshCollider == null)
return;
tex = rend.material.mainTexture as Texture2D;
startUV = hit.textureCoord;
startUV.x *= tex.width;
startUV.y *= tex.height;
}
if (!Input.GetMouseButton(0))
return;
if (!Physics.Raycast(Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition), out hit))
return;
endUV = hit.textureCoord;
endUV.x *= tex.width;
endUV.y *= tex.height;
Draw(endUV, startUV);
}
void Draw(Vector2 endPoint, Vector2 startPoint)
{
for (int i = 0; i < texturePixelsColors.Length; i++)
{
texturePixelsColors[i] = new Color(1, 1, 1);
}
x0 = (int)startPoint.x;
y0 = (int)startPoint.y;
int dx = (int)(endPoint.x - x0);
int dy = (int)(endPoint.y - y0);
int w = Mathf.Abs(dx);
int h = Mathf.Abs(dy);
int x1 = x0, y1 = y0;
var xval = dx > 0 ? 1 : -1;
var yval = dy > 0 ? 1 : -1;
bool isGradualSlope = w > h;
if (isGradualSlope)
{
int accumulator = 2 * h - w;
for (int i = 0; i < w - 1; i++)
{
x1 += xval;
if (accumulator < 0)
{
accumulator += 2 * h;
}
else
{
y1 += yval;
accumulator += 2 * (h - w);
}
var textureIndex = GetIndex(new Vector2Int(x1, y1), new Vector2Int(width, height));
texturePixelsColors[textureIndex] = rc;
}
}
else
{
int accumulator = 2 * w - h;
for (int i = 0; i < h - 1; i++)
{
y1 += yval;
if (accumulator < 0)
{
accumulator += 2 * w;
}
else
{
x1 += xval;
accumulator += 2 * (w - h);
}
var textureIndex = GetIndex(new Vector2Int(x1, y1), new Vector2Int(width, height));
texturePixelsColors[textureIndex] = rc;
}
}
texture.SetPixels(texturePixelsColors);
texture.Apply();
mat.mainTexture = texture;
}
int GetIndex(Vector2Int coord, Vector2Int size)
{
return size.x * coord.y + coord.x;
}
}

참고
이득우의 게임 수학 : 네이버 도서
네이버 도서 상세정보를 제공합니다.
search.shopping.naver.com
https://www.markwrobel.dk/post/amiga-machine-code-letter12-linedraw/
https://www.middle-engine.com/blog/posts/2020/07/28/bresenhams-line-algorithm
'study > math' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [이득우 게임수학] 아핀공간 (0) | 2024.07.03 |
|---|---|
| [이득우 게임수학] 역행렬 (0) | 2024.06.30 |
| [이득우 게임수학] 행렬의 설계 (0) | 2024.06.26 |
| [이득우 게임수학] 행렬 (0) | 2024.06.17 |
| [이득우 게임수학] 선형성과 선형변환 (0) | 2024.06.09 |




댓글